Custom Medals
Custom Medals

The FNMT-RCM, alongside their traditional production of banknotes, coins and stamped effects (letterheads) created using the most advanced technology, has now added new generation products such as smart cards, identification documents, electronic certificates, etc to its range of products.
However, it has not wanted to put aside product lines involving artisan and artistic designs which have always gained it well-earned prestige throughout its long history that dates back to at least the end of the 15th century.
Of these activities, the production of medals is the one that stands out.
The range of possibilities it encompasses is practically unlimited, given the artistry required by their manufacture. However, the text below refers specifically to the most usual products created by the FNMT-RCM which is always ready to adapt to the specific needs of each customer.
Just as with coins, medals are usually metal discs (gold, silver, copper. etc.) that are struck on both sides.
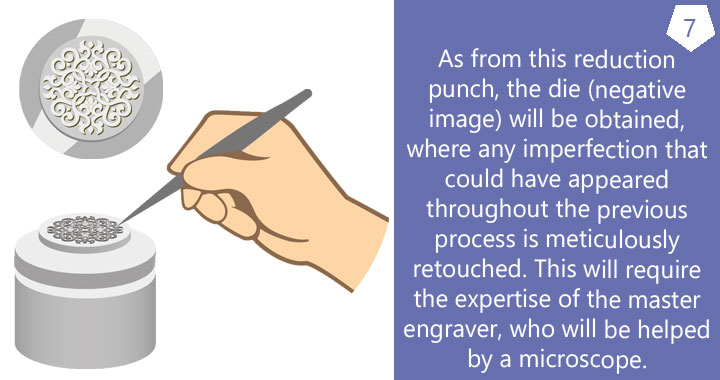
A medal is a product that emerges from an idea that is gradually conveyed into an artistic language by means of a series of steps that include the design, the modelling (bas-relief) and the striking of the piece. All of these stages are overseen by the artist (engraver) who provides the appropriate guidance to ensure that the final result is one of great quality. The size of the piece (up to 80 mm in diameter), as well as the relief that is modelled (1 tenth of a millimetre to 3 millimetres in thickness), are part of this process.
The FNMT-RCM strikes medals in gold, silver, copper etc. in a range of finishes and diameters. The finish may be highly polished, matte or with patination (silver and copper), with the possibility of combining the first two finishes in the same piece.
The thickness of the medal is the result of the aesthetic and technical requirements of the striking process and is related to its diameter. Although any diameter between 10 and 80 mm may be manufactured, there are some which, for reasons of standardisation, are more economical to produce.
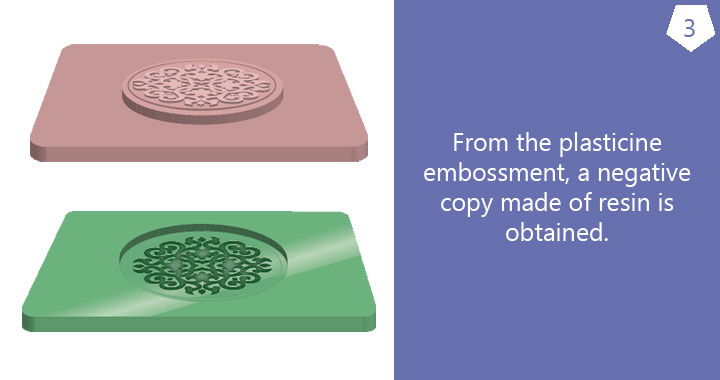
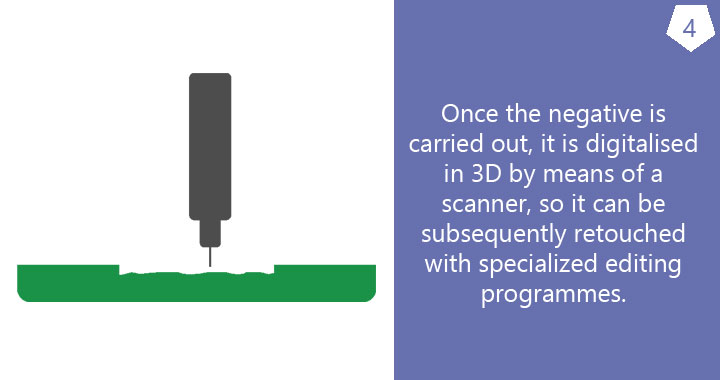
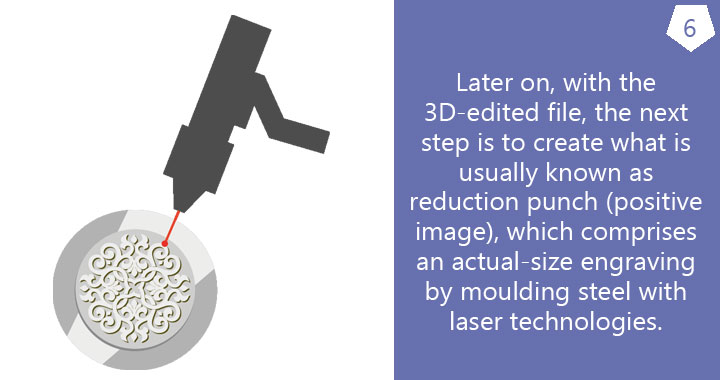
Prior to the striking process, the dies have to be manufactured. Once they have been produced, they can be used to strike medals of the same size in different metals and for subsequent strikings.